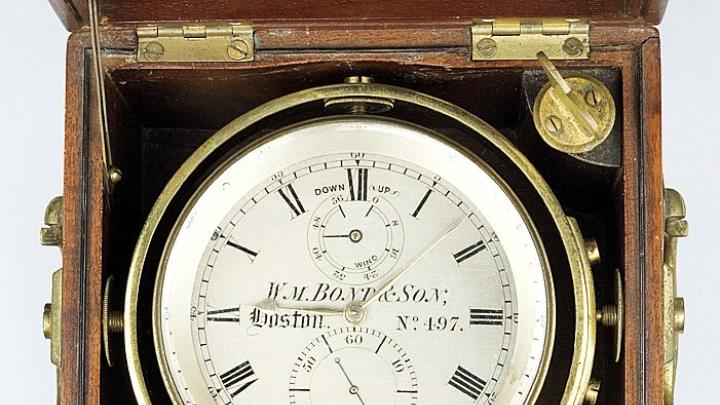
Using relatively simple tools, early explorers navigated the archipelagos of the southern Pacific and many other dangerous, uncharted corners of the world. Finding Our Way: An Exploration of Human Navigation traces such endeavors by mariners from the fourteenth to the nineteenth centuries. Items both functional and beautiful are on display: compasses, scaled models of canoes, nautical atlases, and astrological texts, as well as an astrolabe, octant, and cross-staff. The marine chronometer (above) is a very precise clock made by William Bond & Son, Boston, circa 1860. Navigators used them “to keep the time at their port of origin or at a designated starting point, such as Greenwich, England,” says Sara J. Schechner, Wheatland curator of the Collection of Historical Scientific Instruments. “By comparing the local time at their current geographical position with the time on the chronometer, they could find their longitude in hours, minutes, and seconds.”