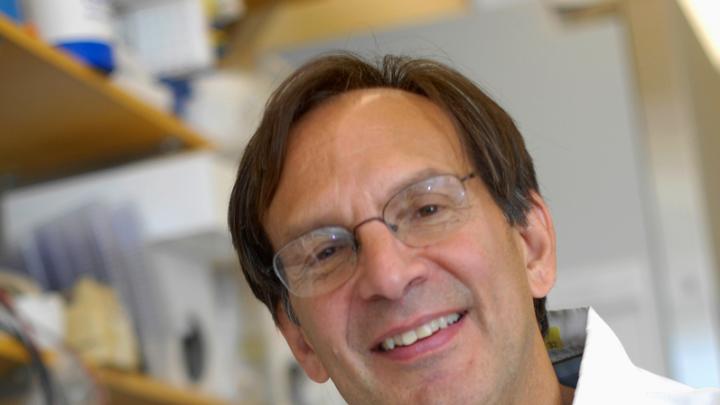
Could a pill provide the benefits of exercise? Sacrilege to some, the thought has nevertheless motivated researchers seeking to treat some of the most perplexing human diseases, from diabetes to Parkinson’s to cancer. Now researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI), led by Harvard Medical School professor Bruce Spiegelman, have isolated a signaling protein that triggers some of the same health benefits as exercise. The results of their work have been posted as an advance online publication by the journal Nature.
The protein, dubbed irisin by the researchers, turns on the genetic machinery that converts white fat tissue into beneficial brown fat, which is thought to burn off excess calories as heat; irisin also improves glucose tolerance and leads to weight loss in obese, prediabetic mice. Speigelman believes irisin could become the basis of a drug that might reach the clinical testing phase in as little as two years because it is a natural substance that is identical in mice and humans, and the effective experimental dose matches that induced by normal exercise. (Irisin levels increase as a result of repeated bouts of prolonged exercise, but not during short-term muscle activity.)
The discovery won't allow people to skip the gym and build muscles by taking irisin supplements, however, because the hormone doesn't appear to make muscles stronger. For now, only exercise can do that.
Irisin was identified during a search for genes and proteins regulated by a master metabolic regulator, PGC1-alpha, that is turned on by exercise and that controls muscle fiber-type switching. Spiegelman's group had discovered PGC1-alpha in previous research.
The National Institutes of Health-funded study merely scratches the surface of irisin's multiple effects, according to the researchers, who are now exploring its potential benefits in metabolic diseases such as diabetes, insulin resistance, and obesity, which constitute a growing epidemic around the world, as well as neurodegenerative illnesses like Parkinson's disease.